Mandatory corporate tax registration in the UAE has become a hot topic, especially as businesses adjust to the evolving tax landscape.
With the UAE’s historically tax-free reputation shifting to align with global norms, understanding corporate tax is no longer optional—it’s crucial for business survival and success.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into corporate tax in the UAE.
From rates and registration processes to exemptions, reliefs, filing, and compliance, we’ve got all your questions covered.
Whether you’re a startup, a small business, or a multinational, you’ll walk away with actionable insights to navigate this important change confidently.
UAE Corporate Tax Landscape
For years, the UAE has been known for its business-friendly environment, with zero personal income tax and minimal corporate tax obligations.
But starting June 1, 2023, the UAE introduced a corporate tax regime as part of its effort to meet global tax transparency standards and diversify its economy.
While this shift may seem daunting, the UAE’s tax system remains one of the most attractive in the world, with low rates and various exemptions. However, compliance is key.
Whether you’re a business owner, financial advisor, or accountant, it’s vital to understand the corporate tax system to avoid penalties and optimize your tax strategy.
UAE Corporate Tax Rates:
Let’s cut to the chase: corporate tax in the UAE is structured to be straightforward and business-friendly.
Here’s a breakdown of the corporate tax rates:
0% for taxable income up to AED 375,000
This threshold is designed to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), allowing smaller businesses to continue thriving.
9% for taxable income above AED 375,000
A highly competitive rate compared to global corporate tax standards, which often exceed 20%.
Different rates for large multinational companies
Businesses falling under the OECD Pillar Two framework, with consolidated global revenues of €750 million or more, may be subject to higher rates in compliance with global minimum tax rules.
Why the UAE Corporate Tax Rate is Competitive
The UAE’s 9% rate is one of the lowest in the world. For context:
- The global average corporate tax rate in 2023 was approximately 23.5%.
- Neighboring Gulf countries like Saudi Arabia and Oman levy corporate tax rates of 20% and 15%, respectively.
Here’s a comparison of corporate tax rates for 20 first-world countries, including their minimum and maximum rates:
| Country | Minimum Corporate Tax Rate | Maximum Corporate Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| UAE | 0% | 9% |
| Ireland | 12.5% | 25% |
| Singapore | 17% | 17% |
| Hong Kong | 8.25% | 16.5% |
| Switzerland | 11.9% | 21.6% |
| United Kingdom | 19% | 25% |
| Netherlands | 15% | 25.8% |
| Canada | 9% | 26.5% |
| Germany | 15% | 29.9% |
| Australia | 25% | 30% |
| United States | 21% | 35% |
| Japan | 23.2% | 29.74% |
| France | 25% | 25% |
| Sweden | 20.6% | 20.6% |
| Norway | 22% | 22% |
| Denmark | 22% | 22% |
| Finland | 20% | 20% |
| Belgium | 25% | 25% |
| Italy | 24% | 27.9% |
| Spain | 25% | 25% |
Who will be required to register for UAE corporate tax?
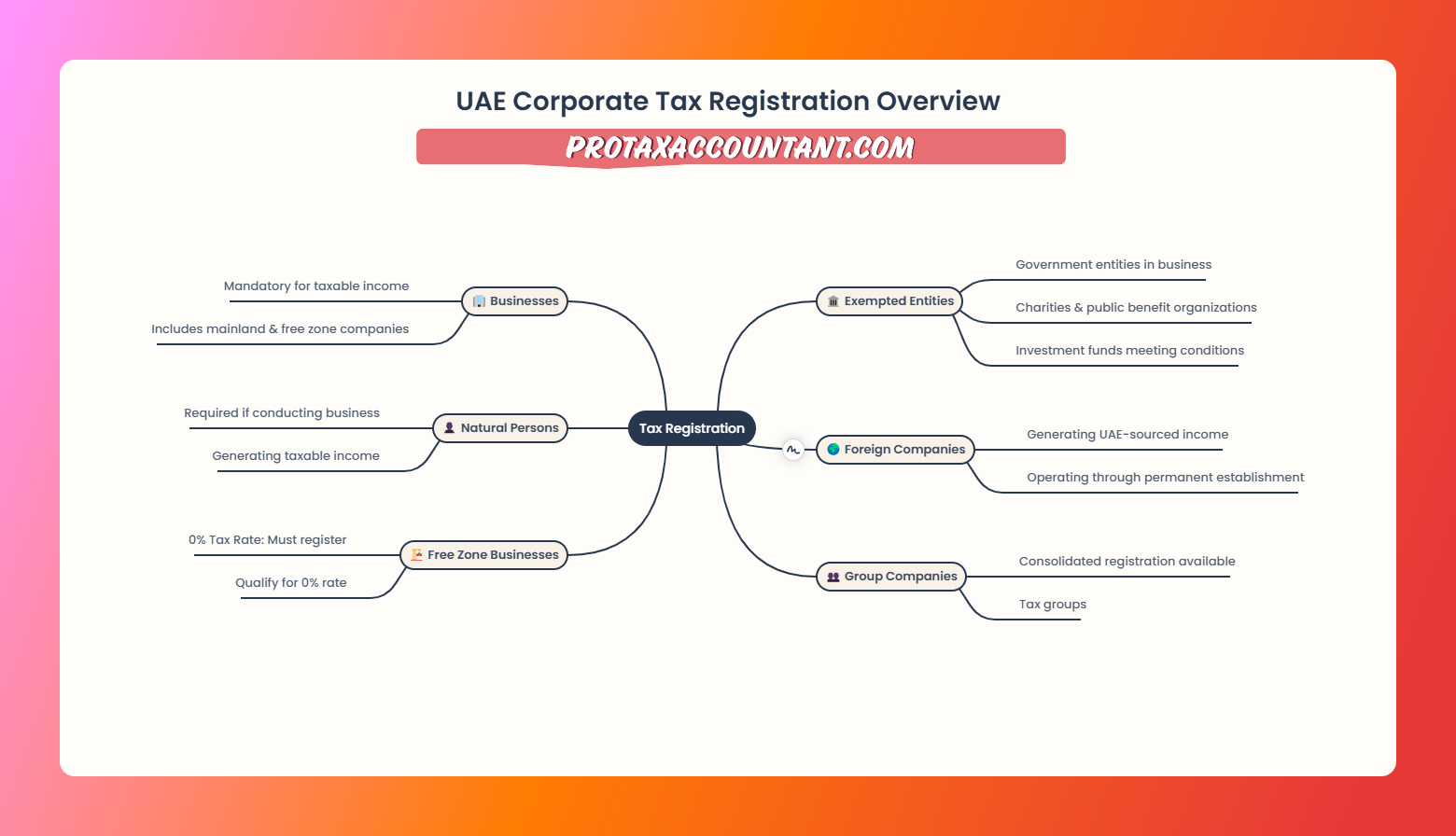
Mandatory corporate tax registration in the UAE is applicable to all taxable persons.
They will be required to register for UAE corporate tax and obtain a corporate tax registration number.
Non-resident persons earning state-sourced income that do not have a permanent establishment or nexus in the UAE do not need to register.
This is because they will not have a corporate tax liability in the UAE, and their home jurisdiction will have primary taxing rights.
Persons seeking to be exempt from corporate tax upon application to the Federal Tax Authority (for example,
an investment fund seeking to be treated as a qualifying investment fund) must first register with the Federal Tax Authority before they can make an application to be exempt from corporate tax.
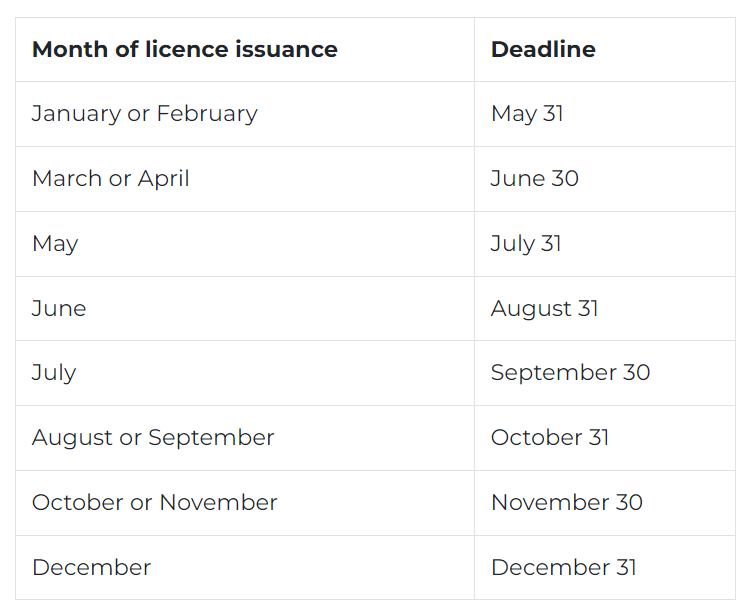
Mandatory Corporate Tax Registration deadline
Registration deadlines are structured based on the original month of incorporation for businesses, irrespective of the year.
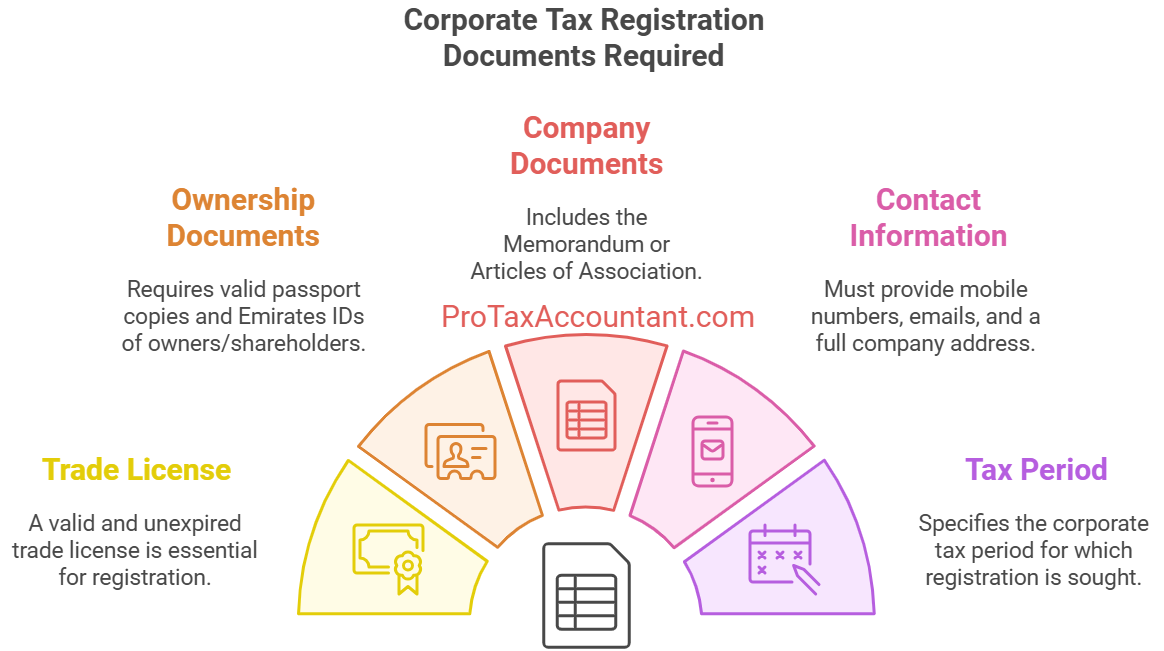
Corporate Tax Registration Requirements
-
- Copy of Trade License (must not be expired).
-
- Passport copy of the owners/partners/shareholders who own the license (must not be expired).
-
- Emirates ID of the owners/partners/shareholders who owns the license (must not be expired).
-
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) or Article of Association (AOA).
-
- Concerned person’s contact details (Mobile Number and email).
-
- Contact details of the company (complete address and P.O. Box).
-
- Corporate Tax Period.
Procedures and Steps
-
- Create an account on Emaratax portal by registering with your email ID and Phone number or login using your existing ID and password.
-
- Create your taxable person or select the relevant taxable person from the taxable person list
-
- You will see the option to register for Corporate Tax. Please select this option and complete your registration.
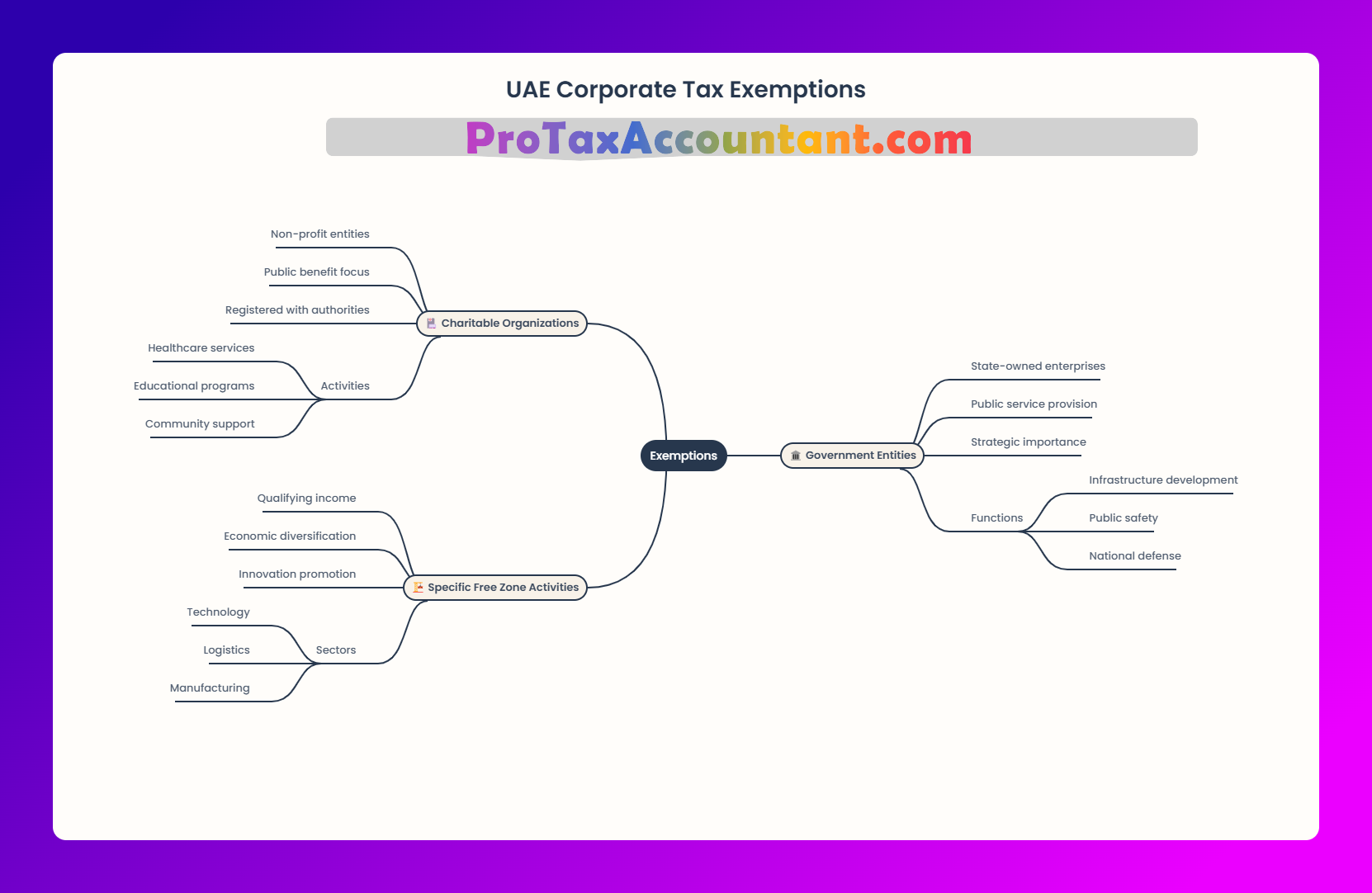
Exemptions:
Who Doesn’t Need to Pay Corporate Tax?
While many businesses are subject to corporate tax, the UAE offers several exemptions to maintain its reputation as a global business hub.
Key Corporate Tax Exemptions
-
Free Zone Businesses
Free zone entities that meet specific compliance requirements (such as not conducting business with mainland UAE) can enjoy a 0% corporate tax rate. -
Government Entities
Government entities and their subsidiaries are exempt from corporate tax. -
Extractive Businesses
Oil and gas companies taxed under existing emirate-level regulations are not subject to the federal corporate tax regime. -
Public Benefit Organizations
Non-profits and charities registered as public benefit organizations are exempt from corporate tax. -
Investment Income
Dividends, capital gains, and certain other investment income earned by UAE-based businesses from domestic or qualifying foreign entities are exempt.
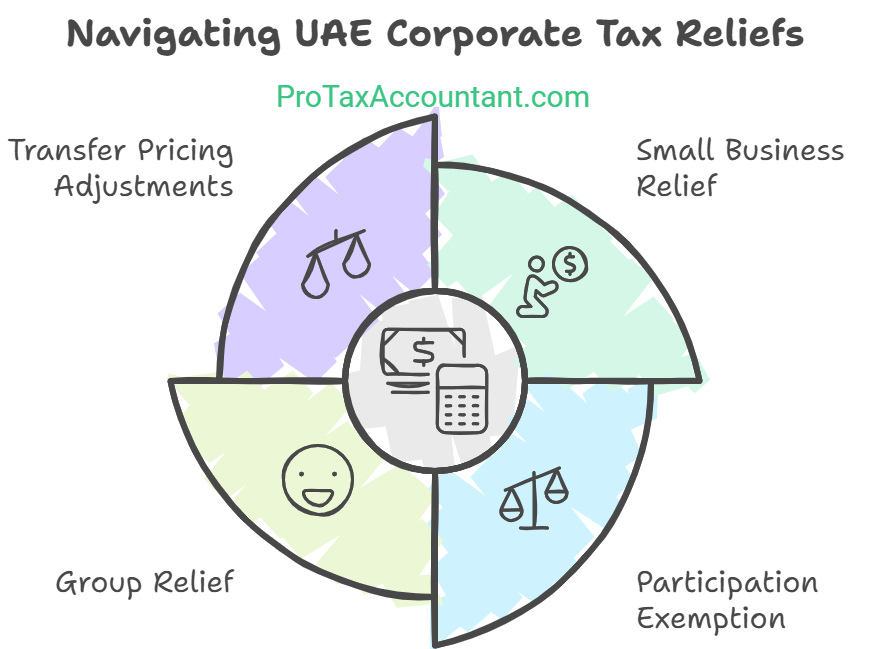
Corporate Tax Reliefs:
Lowering Your Tax Burden
To encourage economic growth and reinvestment, the UAE offers various corporate tax reliefs. Let’s explore how your business can reduce its taxable income.
1. Small Business Relief
Businesses with revenue below AED 3 million per year can benefit from small business relief, aligning them with the 0% corporate tax bracket.
2. Participation Exemption
If a UAE business owns at least 5% of shares in a foreign subsidiary, income earned from dividends or capital gains is tax-exempt.
3. Group Relief
Corporate tax laws allow businesses to form a tax group, consolidating profits and losses across entities. The benefit? You pay tax only on the net consolidated profit.
4. Transfer Pricing Adjustments
Transfer pricing refers to transactions between related entities. The UAE’s transfer pricing rules allow businesses to avoid double taxation and ensure fair valuation.
Corporate Tax Filing:
Deadlines and Requirements
Filing corporate tax returns is one of the most crucial aspects of compliance. Here’s what you need to know:
Annual Filing Deadline
Corporate tax returns must be filed annually, with the exact deadline determined by your financial year. For most businesses:
- Financial year ending December 31: Filing deadline is June 30 of the following year.
What to Include in Your Tax Return
- Audited financial statements
- Breakdown of taxable income
- Details of any tax reliefs or exemptions claimed
Penalties for Late Filing
Failing to file your corporate tax return on time can result in hefty fines, starting at AED 10,000 and escalating based on the delay period.
Compliance:
Staying Ahead of UAE Corporate Tax Rules
Compliance is non-negotiable under the new corporate tax regime. Here’s how businesses can stay compliant:
1. Maintain Accurate Records
The UAE mandates that businesses keep financial records for at least 7 years. These should include:
- Financial statements
- Invoices
- Bank statements
2. Conduct Regular Audits
Audited financial statements are often required for tax filing. Work with certified auditors to ensure accuracy and transparency.
3. Monitor Regulatory Updates
The FTA regularly updates tax rules and regulations. Subscribe to their notifications or work with a tax consultant to stay informed.
4. Leverage Technology
Use accounting software that integrates tax compliance features, helping you track taxable income and generate reports.
FAQs
When does Mandatory Corporate Tax Registration in the UAE is applicable?
All Taxable Persons must be registered before they file their first Corporate Tax Return.
The Federal Tax Authority may register a taxable person who is not otherwise registered, at their discretion.
Is there a registration threshold for UAE Corporate Tax?
There is no registration threshold for UAE Corporate Tax.
How do I register for UAE corporate Tax?
Taxable persons will be able to electronically register for UAE corporate tax through the EmaraTax Portal.
I am already registered for VAT purposes. Do I have to register for UAE corporate tax?
Yes. Taxable persons will be required to register for UAE corporate tax (and update their details, if required), even if they are already registered for VAT.
Will Mandatory Corporate Tax Registration in the UAE be required for exempt businesses or having no tax liability?
All taxable persons, including those with no corporate tax liability, will be required to register for corporate tax and obtain a corporate tax registration number.
Public and qualifying private pension funds and social security funds, qualifying investment funds, and juridical persons owned by certain exempt persons will also need to register for corporate tax before they can be exempt from corporate tax.
Qualifying public benefit entities that are listed in Cabinet Decision No. 37 of 2023 or any subsequent relevant decisions must also register for corporate tax.
Government entities, government-controlled entities, and extractive natural and non-extractive natural resource businesses that meet the relevant conditions in the corporate tax law must register for corporate tax if they conduct a taxable business.
Where a natural person conducts multiple businesses that are subject to corporate tax, does each of these businesses need to register / file corporate tax returns separately?
A natural person who conducts multiple taxable businesses will be considered as one single taxable person for UAE corporate tax purposes, irrespective of how many taxable businesses or business activities he/she undertakes.
This means that each natural person should register for corporate tax once and prepare a single corporate tax return, which includes the income and expenses from all of their taxable businesses.
Will a UAE company with several UAE branches be required to register each branch separately for UAE corporate tax?
No, because branches do not have a separate legal personality and are treated as one and the same person as their UAE ‘head office’.
The UAE company will need to include details of all of their UAE branches within the registration form.
Will individual partners in an incorporated partnership be required to register for corporate tax separately?
This depends on the status of each partner in the unincorporated partnership.
Natural persons who are partners in an incorporated partnership through which they are seen as conducting a taxable business will each be required to register for corporate tax individually.
The same is true for foreign legal entities where the activities performed by or through the incorporated partnership give rise to a permanent establishment in the UAE for the foreign partners.
Domestic legal entities and any other partner in an unincorporated partnership that is already registered for corporate tax purposes as a resident or non-resident person will not have an additional corporate tax registration requirement by virtue of being a partner in an unincorporated partnership.
If a resident juridical person’s revenue is below AED 3 million for a tax period, will it need to register for corporate tax?
Yes, any resident juridical person will need to register for corporate tax regardless of its level of revenue.
Under what circumstances can a business deregister for corporate tax?
A natural person or legal entity can apply to the Federal Tax Authority to deregister for corporate tax if they cease to conduct their business or cease to exist, respectively, provided all tax returns (including the tax return for the tax period up to and including the date of cessation) have been filed and all corporate tax and any administrative penalties due have been settled.
How to Register for Free.
Please contact us for free guidance on registration.