Understanding the difference between cash and accrual accounting is crucial for any small business owner.
These two methods serve as the foundation for how you report your financial transactions, impacting everything from tax obligations to business insights.
In this blog, we’ll break down these concepts in simple terms, explore their advantages and disadvantages, and help you determine which method might be best for your business.
What is an accounting method or basis of accounting?
What It Means
An accounting method, or basis of accounting, refers to the set of rules you follow when reporting your financial transactions.
Essentially, it defines how and when you recognize income and expenses in your financial statements.
Why It Matters
Choosing the right accounting method is vital because it affects how your business’s financial health is portrayed.
For instance, if you report income based on cash received, it may look different from reporting income based on when a sale is made.
This choice can influence everything from tax calculations to management decisions.
“The way you account for your transactions can significantly impact your business’s financial picture.” – Investopedia
What is the Cash Basis of Accounting?
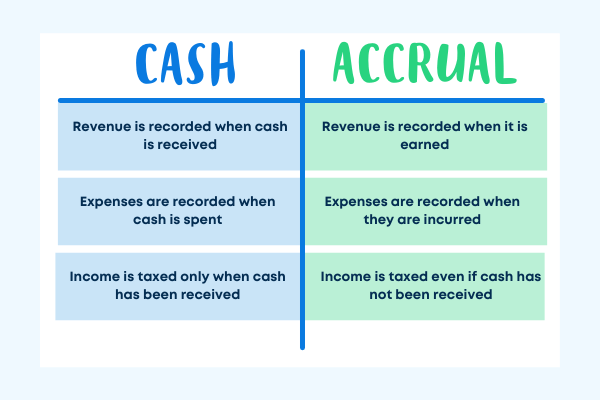
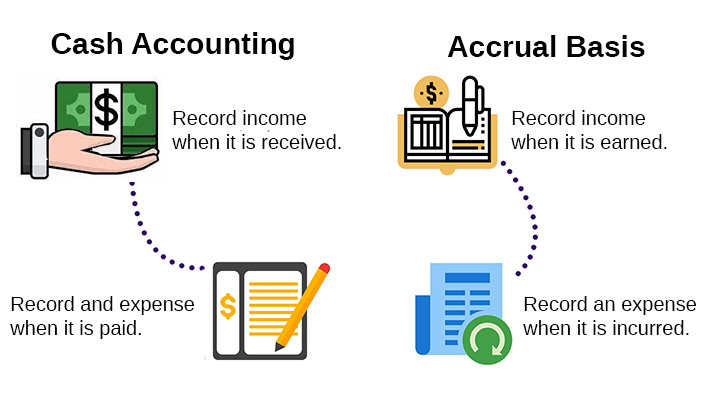
The cash basis of accounting records income when cash is actually received and expenses when they are paid.
This means that if you send an invoice but haven’t received payment yet, that income isn’t counted until the money is in your bank account.
Why It Matters
This method is straightforward and easy to manage, making it ideal for small businesses with simple transactions.
It gives a clear picture of cash flow—how much money is actually available at any given time.
Example:
If you own a small bakery and sell a cake for AED 200 but don’t receive payment until the following month, you won’t record that sale until the payment is received.
This keeps your books simple but may not give a complete picture of your sales performance over time.
Pros and Cons of Cash Basis Accounting

Pros:
Simple to understand and implement.
Provides a clear view of cash flow.
You only pay taxes on income that has been received.
Cons:
Doesn’t provide an accurate picture of overall financial health.
May not comply with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for larger businesses.
“Cash basis accounting is often favored by small businesses due to its simplicity.” – BDC
What is the Accrual Basis of Accounting?
What It Means
The accrual basis of accounting records income when it is earned (when a product or service is delivered) and expenses when they are incurred (when you receive goods or services), regardless of when cash changes hands.
Why It Matters
This method provides a more accurate picture of your business’s financial performance because it matches revenue with the expenses incurred to generate that revenue.
It’s particularly useful for businesses that offer credit or have long-term projects.
Example:
If you run a web design company and complete a project worth AED 5,000 in December but don’t receive payment until January, under accrual accounting, you would record that AED 5,000 as revenue in December.
This gives a better representation of your earnings for that month.
Pros and Cons of Accrual Basis Accounting

-
- Pros:
-
- Provides a more accurate view of financial performance.
-
- Matches income with related expenses.
-
- Useful for businesses with inventory or those that offer credit.
-
- Pros:
-
- Cons:
-
- More complex than cash basis accounting.
-
- Requires careful tracking of accounts receivable and payable.
-
- Cons:
“Accrual accounting gives a clearer picture of business finances by recognizing revenues and expenses when they occur.” – Forbes
Are There Exceptions?
Yes! Both methods have exceptions that can complicate matters:
-
- Cash Basis Exceptions:
-
- Not all money received counts as income. For example, refunds from vendors would be considered negative income.
-
- Some purchases need to be capitalized instead of being treated as immediate expenses (like equipment or inventory).
-
- Cash Basis Exceptions:
-
- Accrual Basis Exceptions:
-
- Certain small businesses may opt to use cash basis accounting if they meet specific criteria set by tax authorities.
-
- Accrual Basis Exceptions:
Which Method is Suitable for My Business?
What It Means
Choosing between cash and accrual accounting depends on various factors such as the size of your business, complexity of transactions, and whether you have external stakeholders like investors.
Why It Matters
Selecting the right method can save time, reduce errors, and provide better insights into your financial health.
Example:
If you’re a small sole proprietor with minimal transactions (like a freelance graphic designer), cash basis accounting may be sufficient due to its simplicity.
However, if you’re running a larger company with multiple clients and projects (like an advertising agency), accrual accounting could provide better insights into profitability and cash flow management.
“The choice between cash and accrual accounting should align with your business model and operational needs.” – Business News Daily
What UAE Tax Law and Cash vs Accrual Accounting
In the UAE, both cash basis and accrual basis accounting are acceptable methods under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
However, there are specific guidelines regarding which method to use based on the size and nature of your business:
-
- Small Businesses: Smaller businesses often prefer cash basis accounting due to its simplicity.
-
- Larger Businesses: Businesses with significant inventory or complex transactions are generally required to use accrual accounting to comply with tax regulations.
For detailed guidance on VAT compliance in relation to these accounting methods, it’s advisable to consult local tax professionals or refer to resources provided by the Federal Tax Authority.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between cash and accrual accounting is crucial for any small business owner looking to manage their finances effectively.
Each method has its pros and cons, making it essential to choose one that aligns with your business model and operational needs.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your existing processes, having clarity on these concepts will empower you to make informed decisions about your financial reporting.
How Pro Tax Accountant Can Help
Navigating the complexities of accounting methods can be challenging.
At Pro Tax Accountant, we specialize in providing tailored accounting and tax services for small businesses.
Our team can help you choose the right accounting method based on your unique needs while ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Let us handle the numbers so you can focus on growing your business!